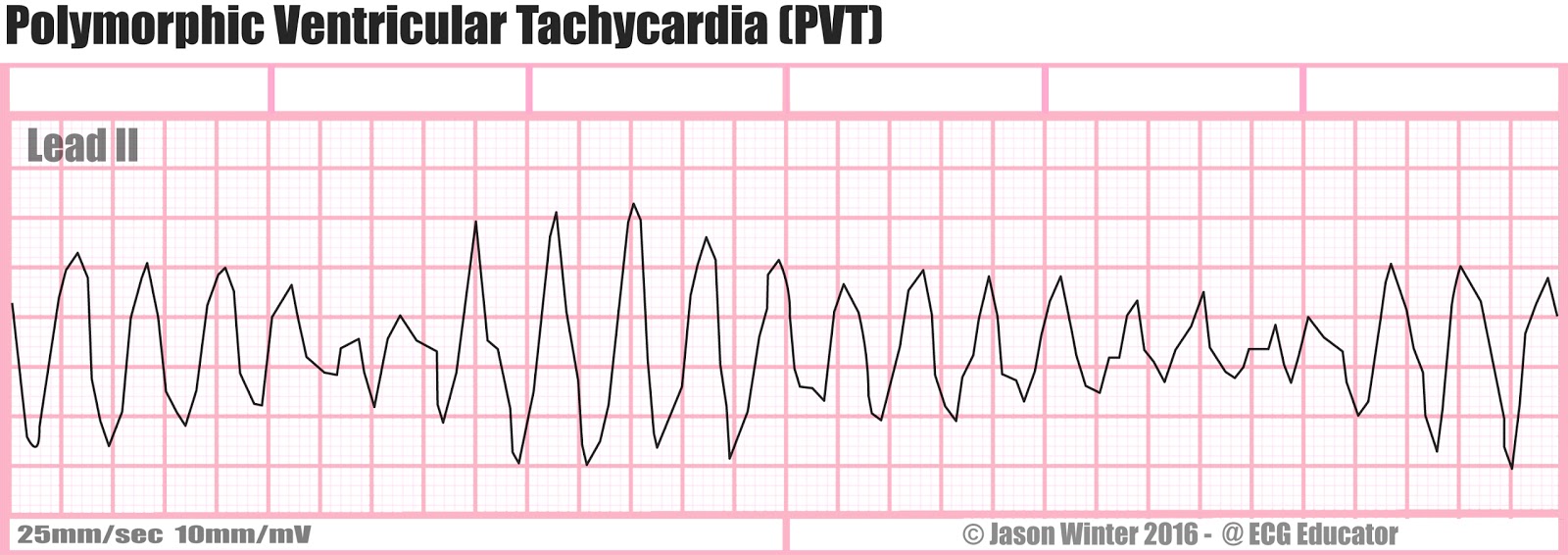
Pvt Shockable Rhythm

Position Of The Paddles

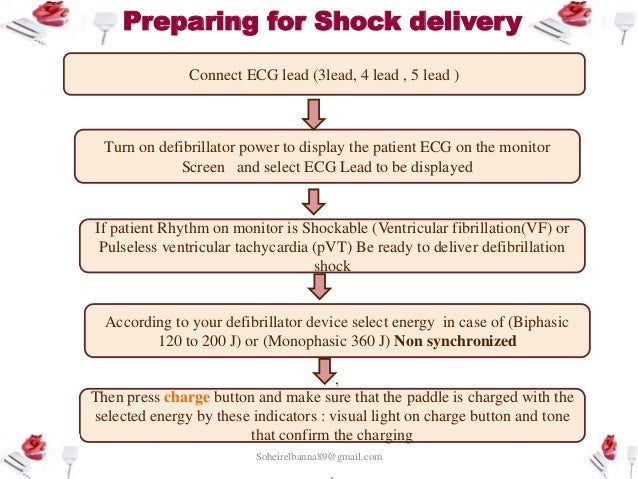
My Emcc Learning Journey Emcc Understanding The Sequence Of Shock Cpr Drug Shock
Www Vdh Virginia Gov Content Uploads Sites 23 16 05 Car 519 Pdf

Acls Ventricular Fibrillation And Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Guide

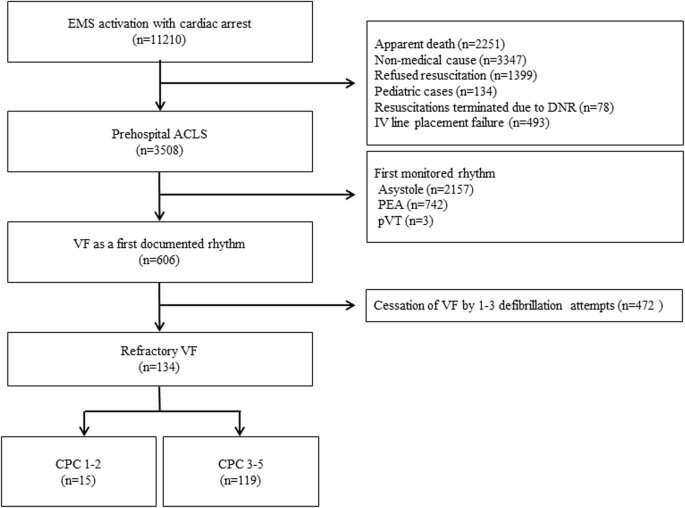
Swiss Medical Weekly Outcome After Out Of Hospital Ventricular Fibrillation Or Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Comparison Of Before And After The Implementation Of The 10 Guidelines In A Single Centre
Crash Cart Part 2 Defibrillator Www Youtu
The proper dosing of epinephrine for VF/pVT is:.

Pvt shockable rhythm. Order by books in e copy from, https://campbellteaching.co.uk/ebooks/ The 4 forms of cardiac arrest are ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, as. Asystole and PEA are also included in the cardiac arrest algorithm but are non-shockable rhythms. Read ECG from printed strip.
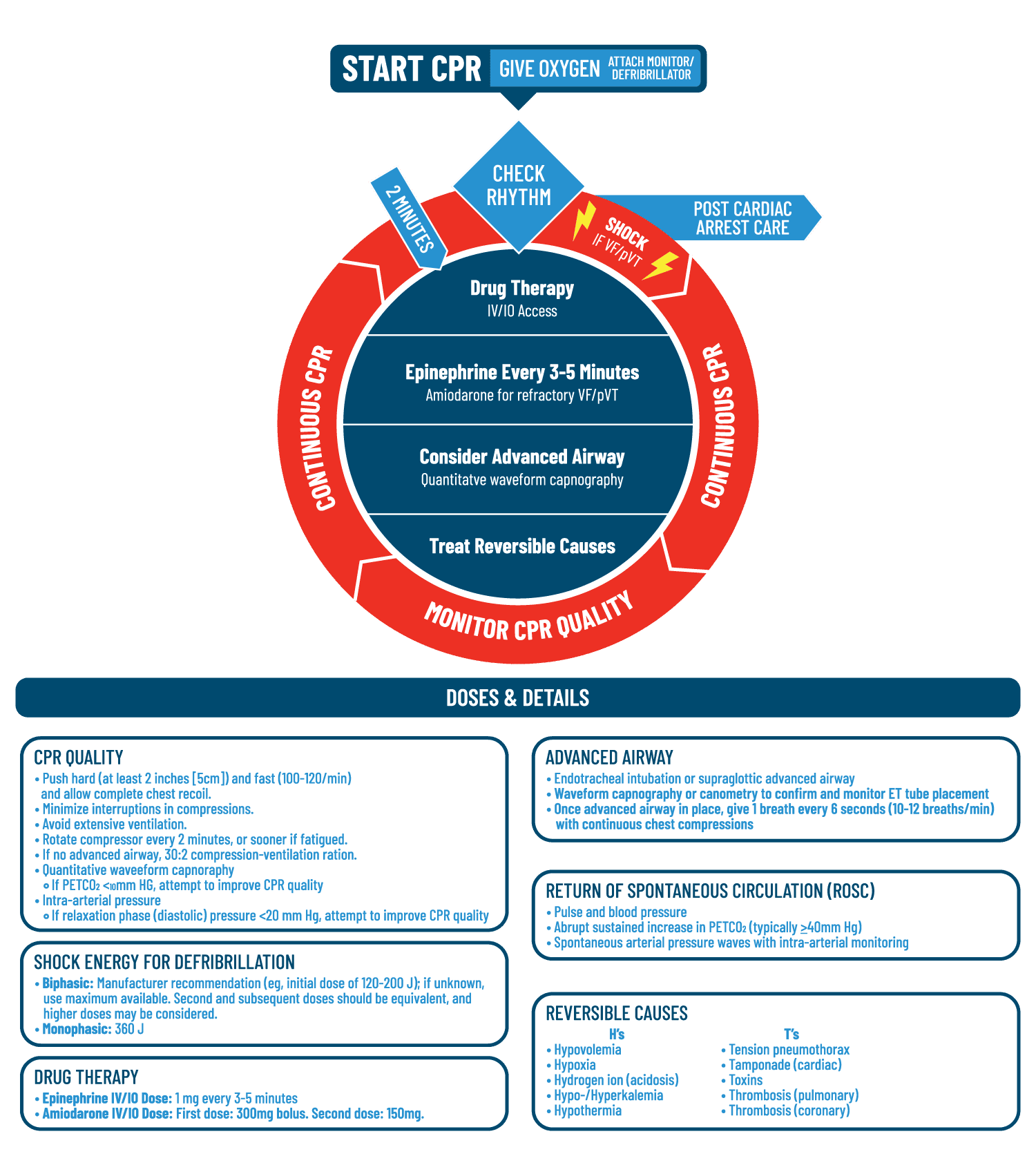
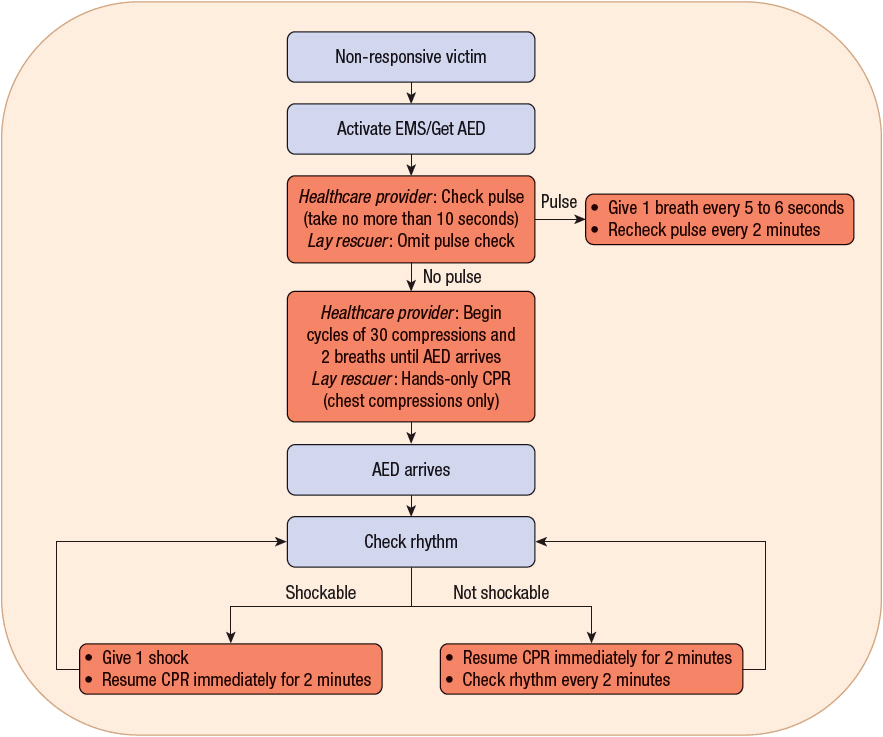
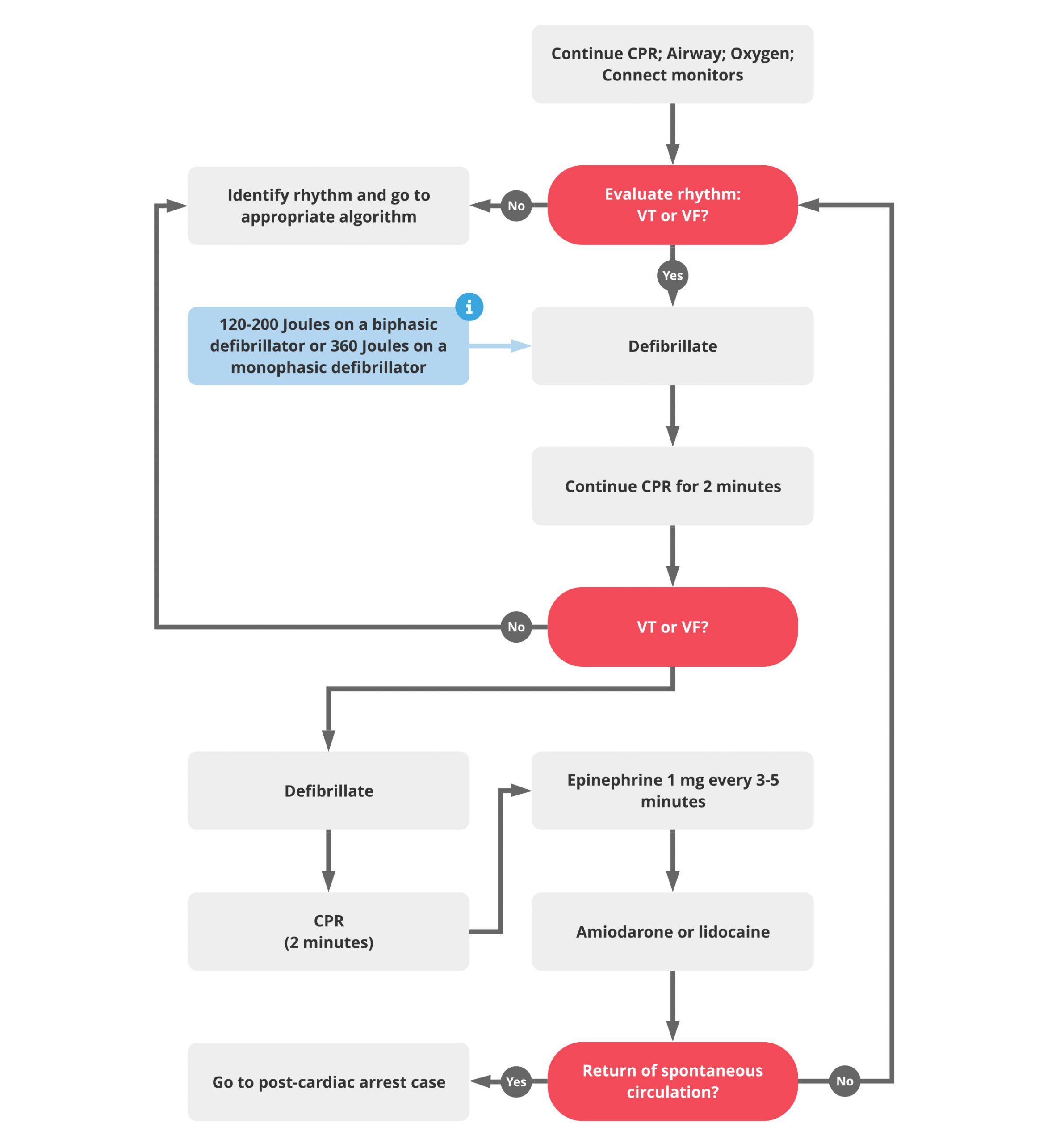
VT is an unstable rhythm. Rhythm check after 2 minutes of CPR (and after every 2 minutes of CPR thereafter) and shock again if indicated. The Cardiac Arrest Algorithm is the most critical algorithm of ACLS.
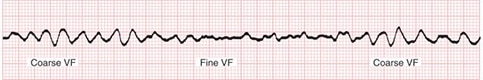
In contrast, you do not shock PEA or asystole, and must follow another pathway of the Cardiac Arrest Algorithm. FVF Fine Ventricular Fibrillation 0.1 mV < amplitude < 0.2 mV Shockable MVT, PVT Ventricular Tachycardia (Monomorphic or Polymorphic) QRS > 1 ms, ventricular or unknown origin. It can occur in short bursts causing few or no symptoms.
300 mg IV/IO bolus. VF and Pulseless VT are shockable rhythms. Concurrently with second round of CPR.
For shockable rhythms, trial protocols have directed that epinephrine be given after the third shock. When you have a patient without a pulse, you must recognize either ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (pVT) as shockable rhythms. Initial non-shockable rhythms (PEA or asystole) account for about two-thirds of adult OHCA with an increasing incidence compared to initial shockable rhythms (VF and pVT) , 21.
When you have a patient without a pulse, you must recognize either ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (pVT) as shockable rhythms. Question 8 / 10. Alternatively it may be sustained, becoming symptomatic and causing unconsciousness, loss of cardiac output and death.
When you have a patient without a pulse, you must recognize either ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (pVT) as shockable rhythms. After the 3rd shock. Shockable rhythms may be the initial rhythm of the cardiac arrest (primary VF/pVT) or may develop during the resuscitation (secondary VF/pVT).
Patients presenting with OHCA due to shockable rhythms such as ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VF/pVT) have a high probability of having coronary artery disease (CAD). The main cause of arrest was a cardiac disease (56.8%). Asystole is a flat-line ECG (Figure 27).
Regular or slightly irregular ventricular rhythm. There may be subtle movement away from baseline (drifting flat-line), but there is no perceptible cardiac electrical activity. Resume compressions immediately SHOCKABLE?.
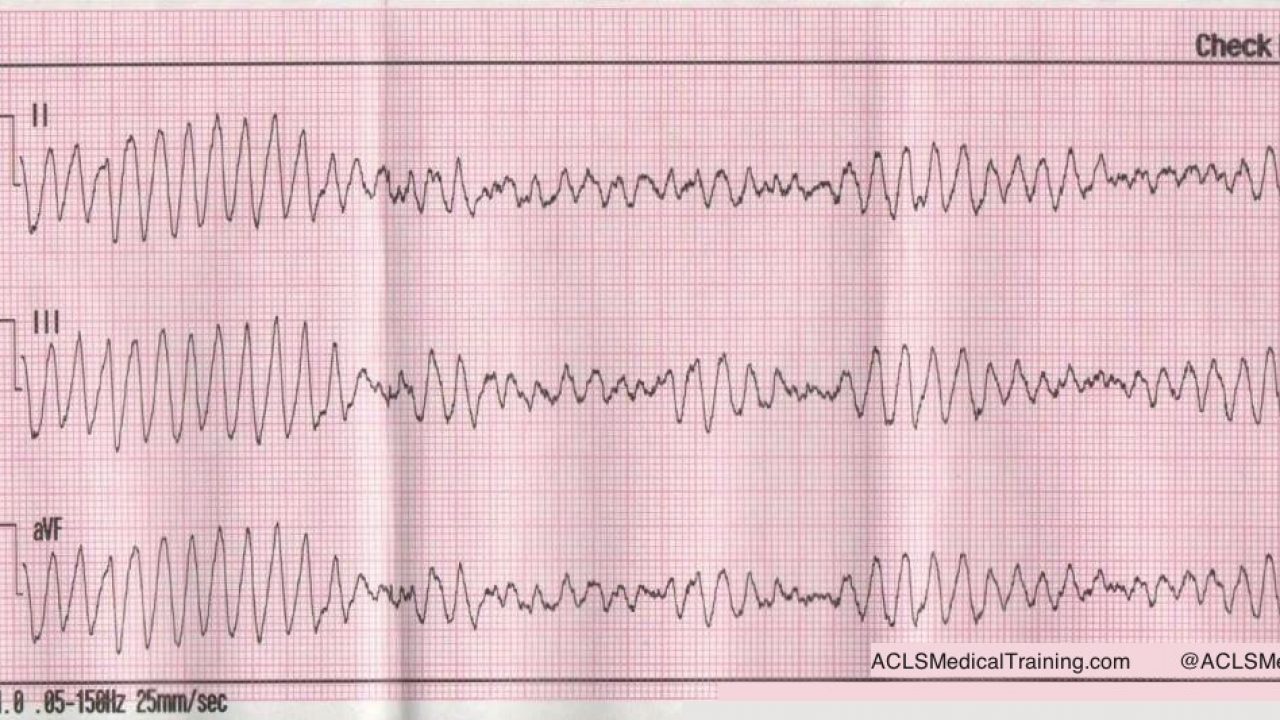
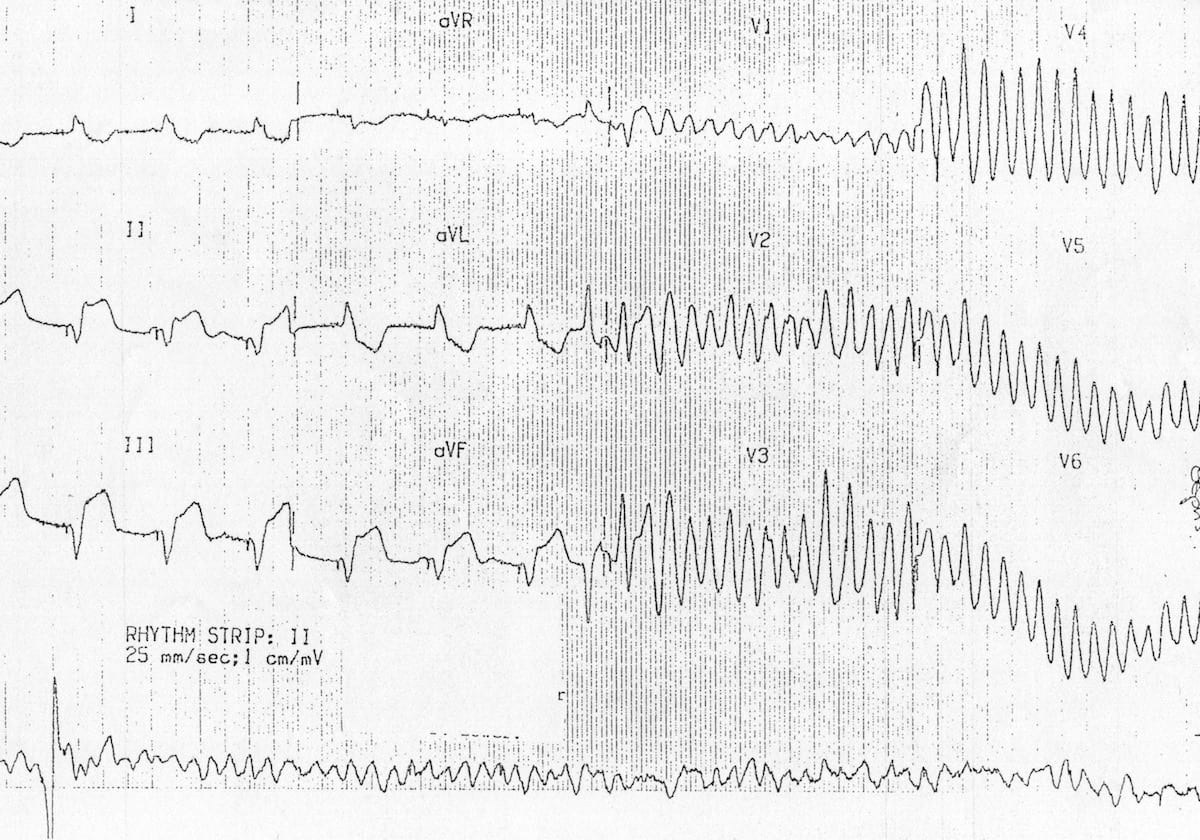
VF (Figure 24) is a rapid quivering of the ventricular walls that prevents them from pumping. If an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) detects a non-shockable rhythm, it won’t allow the rescuer to deliver an electrical shock to. When you have a patient without a pulse, you must recognize either ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (pVT) as shockable rhythms.
If pt is in PEA/Asystole when should Epi be given. When you have a patient without a pulse, you must recognize either ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (pVT) as shockable rhythms. 1 mg IV/IO - repeated every 3 to 5 minutes.
1 to 2 g IV/IO diluted in 10 mL saline over 5 to minutes. During the pulse check it is found that the patient has an organized rhythm but pulses are not palpable -- this is PEA - chest compressions resume immediately. Overall survival after adult OHCA is about 8% , with a worse prognosis with PEA compared to initial shockable rhythms 16, 23–28.
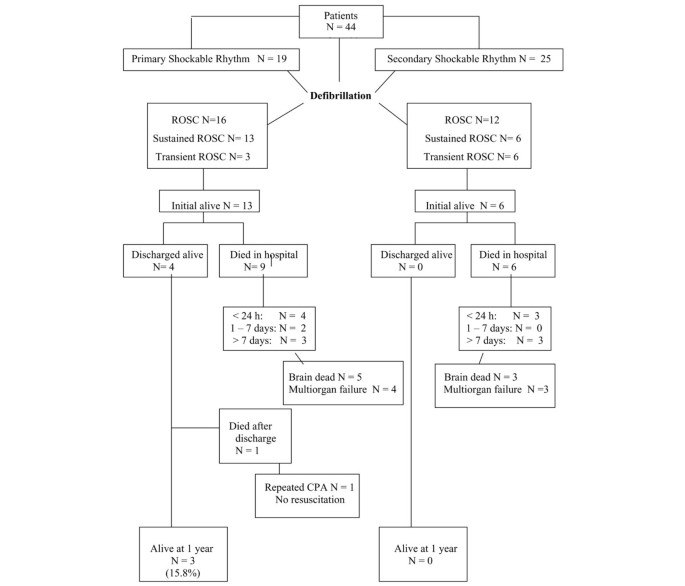
In 17 episodes (42.5%) ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (pVT) was the first documented rhythm, and in 23 (57.5%) it developed during CPR efforts. The treatment of (VF and pulseless VT) Ventricular Fibrillation and Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia is included in the Cardiac Arrest Algorithm. Shockable rhythms have certain characteristics that can be used to distinguish them from non-shockable rhythms.
When should IV/IO access be gained?. The feature extraction component of the AED. The Cardiac Arrest Algorithm is the most critical algorithm of ACLS.
A concern is that several studies have reported a decline in the incidence of VF/PVT over the past few decades. The healthcare provider immediately pushes the shock button and resumes CPR immediately for another two minutes. 2 minutes after first dose of Epinephrine (VF/pVT) When is an advanced airway placed?.
VF/pVT, Asystole/PEA Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Major Points Hypothermia has been studied as a potential therapy for avoiding poor neurologic outcomes post-arrest since the early 00’s. DEFIB immediately If meets one or more criteria below:.
CAD is a common substrate, and its severity is a potential trigger for OHCA, especially in the case of shockable rhythms. 6,7 Although antiarrhythmic medications are commonly administered for VF/VT. The Cardiac Arrest Algorithm is the most critical algorithm of ACLS.
If a shockable rhythm is present, either v-fib or pulseless v-tach, begin the charging sequence on the defibrillator and resume chest compressions until the defibrillator is charged. The landmark studies that documented this phenomenon were performed on comatose patients after an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) with an initial shockable rhythm of ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (pVT). Question 1 / 10.
After shock, immediately begin chest compressions followed by respirations (30:2 ratio) for 2 minutes. Nonshockable rhythms may evolve to shockable ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VF/VT) during the course of resuscitation in ≤25% of patients with OHCA, for whom antiarrhythmic drug use has both pragmatic and public health importance. 22.5), ventricular fibrillation (VF) (Fig.
Survival from cardiac arrest is associated with having a shockable presenting rhythm (VF/pulseless VT) upon EMS arrival. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at the two non-shockable rhythms. Pulseless Electrical Activity Asystole Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) and asystole are related cardiac rhythms in that they are both life-threatening and unshockable.
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) and pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT) are life-threatening cardiac rhythms that result in ineffective ventricular contractions. When should Epi be administered in a VF/pVT. Rhythm check should be done after 2 mins of CPR - minimize interruptions in chest compressions (<10s) - only perform a pulse check if an organized rhythm is present - organized rhythm/palpable pulse = post-arrest care - non-shockable/no pulse = asystole/PEA pathway - shockable rhythm = 1 shock;.
The remaining group of four AEDs highlighted different. The Weighted Importance of Shockable Rhythms to Survival In most medical conditions, identification and treat-ment of an underlying pathogenesis are a fundamen-tal tenant of medical practice and provide improved outcomes. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), and the most salvageable one.
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is the the most important shockable cardiac arrest rhythm. 6.2 NON – SHOCKABLE RHYTHMS This includes asystole and pulseless electrical activity. Patients with VF/pVT have a significant burden of CAD:.
8 Ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia will also occur at some stage during resuscitation in about 25% of cardiac arrests with an initial documented rhythm of asystole or PEA. VF / PVT. The Cardiac Arrest Algorithm is the most critical algorithm of ACLS.
22.6) and pulseless ventricular tachycardia (PVT) are the rhythms most often associated with cardiac arrest. • If no signs of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), go to 10 or 11 • If ROSC, go to Post–Cardiac Arrest Care Go to 5 or 7 VF/pVT Asystole/PEA CPR Quality • Push hard (at least 2 inches 5 cm) and fast (100-1/min) and allow complete chest recoil. For patients with VF/pVT OHCA, CAD is the most common reversible underlying cause.7,9 Pa-.
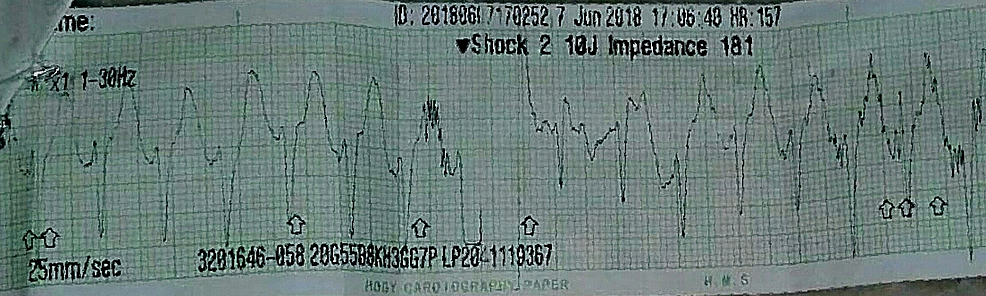
Ventricular Tachycardia, Ventricular Fibrillation, Supraventricular Tachycardia. • Minimize interruptions in. Print strip during pause;.
Asystole, pulseless electrical activity (PEA, formerly known as electromechanical dissociation) (Fig. When should Amio be administered in a VF/pVT. The Cardiac Arrest Algorithm is the most critical algorithm of ACLS.
Much of Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) is about determining the right medication to use at the appropriate time and deciding when to defibrillate. After first shock, during compressions. The ECG will distinguish asystole from ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia and pulseless electrical activity.
Although VF appears as a chaotic and disorganized rhythm, characteristics of the ventricular fibrillation waveform such as amplitude, frequency, and organization can be systematically quantified in real-time. The Cardiac Arrest Algorithm is the most critical algorithm of ACLS. ‘Non-shockable’ means that defibrillation is not an effective treatment for these heart rhythms.
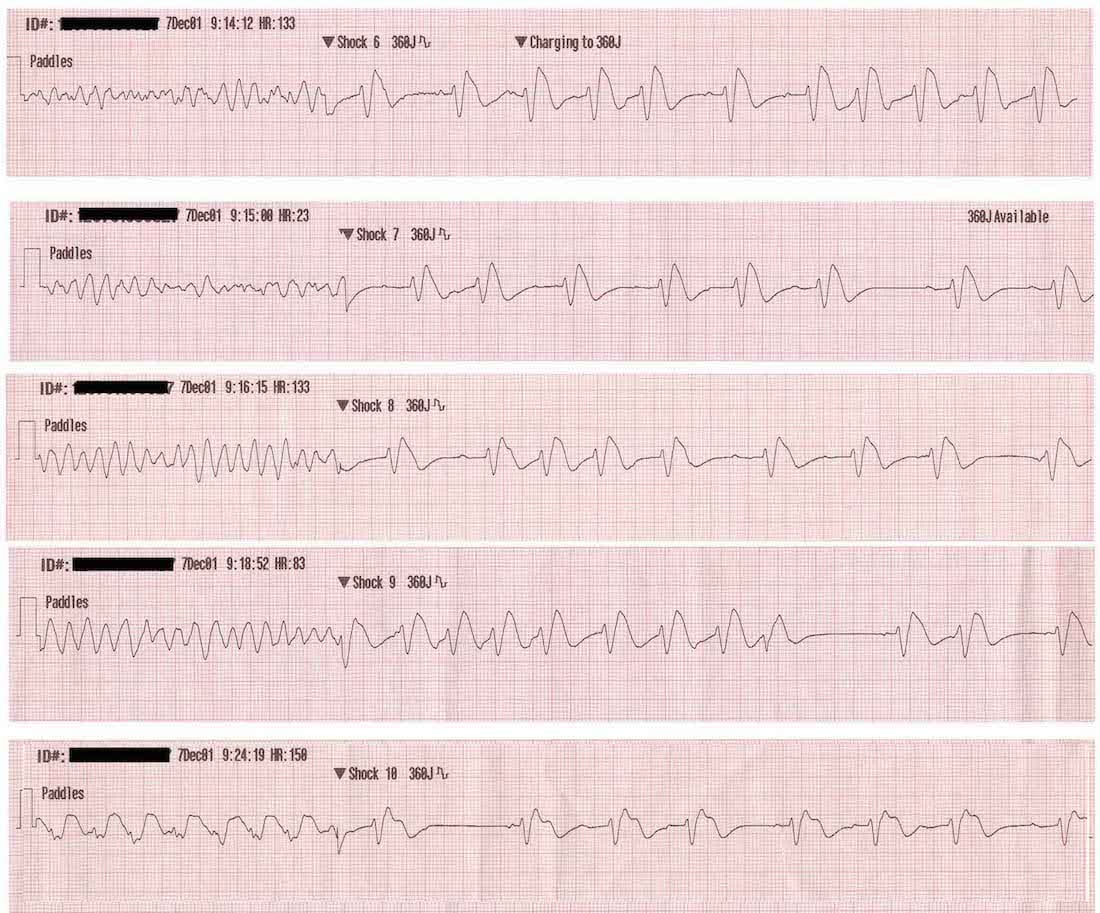
After the 2nd shock. With positive outcomes following cardiac arrest unlikely, an effort has been spent in finding effective strategies to prevent cardiac arrest. VF or pulseless VT – a rhythm check on an AED after 2 minutes of CPR in a victim with VF or pulseless VT will prompt spontaneous charging of the device and prompt the health care provider to “clear” the victim when the AED is ready to deliver the shock.
VF and pulseless VT are shockable rhythms and treated in similar fashion. In contrast, you do not shock PEA or asystole, and must follow another pathway of the Cardiac Arrest Algorithm. Patients with VF/pVT OHCA should be considered at the highest severity of a continuum of acute coronary syndromes.
Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (VF) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (VT). The two "shockable" rhythms are ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia while the two "non-shockable" rhythms are asystole and pulseless electrical activity. The remaining 14 devices showed different behaviours.
Once the child is attached to the monitor or AED, the rhythm should be analyzed and determined to be shockable or nonshockable. Immediate CPR x 2 mins. (Do not check rhythm or pulse) R.
This rapid and irregular electrical activity renders the ventricles unable to contract in a synchronised manner, resulting in immediate loss of cardiac output. The two nonshockable rhythms are p ulseless electrical activity (PEA) and asystole and the two shockable rhythms are pulseless ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrilation. Along with high-quality CPR, emergency medicines and defibrillation are the only two interventions that are likely to restart the arrested heart.
Consider need for. Defibrillation is the definitive treatment for VF/pVT. The shorter the duration of VF/pVT, the more likely that the shock will result in a perfusing rhythm.
How often should Epi be administered. Conduct a rhythm check, making sure the pause in chest compressions is not more than 10 seconds. -- only VF/pVT are shockable;.
In 11 patients (27.5%) three or more shocks were needed to achieve defibrillation. The ventricles suddenly attempt to contract at rates of up to 500 bpm. When you have a patient without a pulse, you must recognize either ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (pVT) as shockable rhythms.
Six AEDs identified as shockable rhythms those PVTs characterized by BPM levels above 180 (PVT1). Acute, chronic, or acute on chronic. During CPR once IV/IO access is established.
THE MANAGEMENT OF CARDIAC ARREST 49 Asystole This is the most common arrest rhythm in children, because the response of the young heart to prolonged severe hypoxia and acidosis is progressive bradycardia leading to asystole. Shockable rhythms (VF/pVT) The first monitored rhythm is VF/pVT in approximately % of both in-hospital 7 and out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OHCAs). The ventricular motion of VF is not synchronized with atrial contractions.
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is the most common initial heart rhythm in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), and the most salvageable one. Ventricular Tachycardia, Ventricular Fibrillation, Supraventricular Tachycardia. Learn More Shockable Rhythms:.
The literature supports prioritizing defibrillation and CPR initially and giving epinephrine if initial attempts with CPR and defibrillation are not successful. If can’t ID rhythm. PEA and asystole are not What are the initial steps upon identification of PEA during resuscitation?.
PVTs are extra heartbeats that disrupt the regular heart rhythm. 1,2 The incidence of initial shockable arrest rhythms, specifically VF and pVT, has been declining. Cardiac arrest rhythms and electrical shock.
When is Amioderone administered?. There are four main heart rhythms that can occur during a cardiac arrest. In patients comatose patients after a non-shockable rhythm (non-VF/pVT) therapeutic hypothermia for 24 hours should be utilized.
Adams, in Veterinary Anaesthesia (Eleventh Edition), 14. Shockable rhythms include pulseless ventricular tachycardia or. Zoll AED Plus) recommended the shock at every kind of PVT.
Downtime ≤ 5 min (electrical phase), coarse VF/PVT, ETCO.

Heartify Algorithms Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Acls Algorithm

2 8 Acls Flashcards Quizlet
Promed Certifications Algorithms Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Acls Algorithm

Jmir The Impact Of A Tablet App On Adherence To American Heart Association Guidelines During Simulated Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Randomized Controlled Trial Siebert Journal Of Medical Internet Research

Promed Certifications Algorithms Adult Cardiac Arrest Acls Algorithm

Cardiac Arrest Pharmacotherapy A Pathophysiologic Approach 9th Ed

Conversion To Shockable Rhythms During Resuscitation And Survival For Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Sciencedirect
Cureus Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Presenting As Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia In A Neonate

3d Als Treatment Algorithm

Jmir The Impact Of A Tablet App On Adherence To American Heart Association Guidelines During Simulated Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Randomized Controlled Trial Siebert Journal Of Medical Internet Research
Ventricular Fibrillation Vf Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis
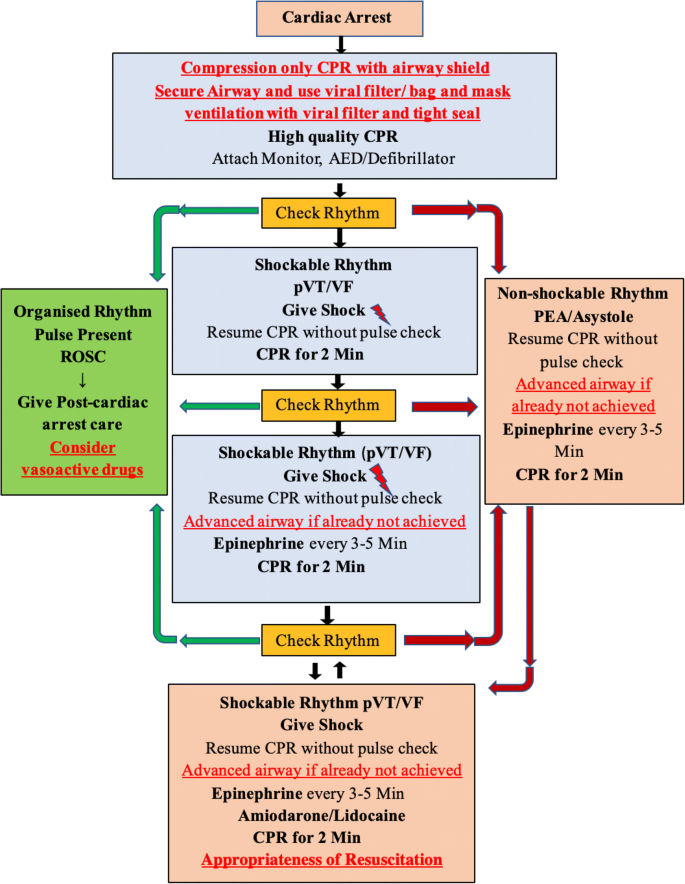
Iap Als Update On Resuscitation Guidelines During Covid 19 Pandemic Springerlink
Www Diva Portal Org Smash Get Diva2 Fulltext01 Pdf

Acls Algorithm Adult Cardiac Arrest
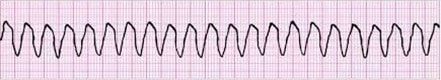
Shockable Rhythms Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular Fibrillation Supraventricular Tachycardia Acls Com

09xe1iwo 2r7bm

Part 3 Adult Basic And Advanced Life Support American Heart Association Cpr First Aid

Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation For In Hospital Events In The Emergency Department A Comparison Of Adult And Pediatric Outcomes And Care Processes Abstract Europe Pmc

Shockable Rhythms Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular Fibrillation Supraventricular Tachycardia Acls Com

Part 5 Adult Basic Life Support And Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Quality Circulation

Jmir The Impact Of A Tablet App On Adherence To American Heart Association Guidelines During Simulated Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Randomized Controlled Trial Siebert Journal Of Medical Internet Research
2
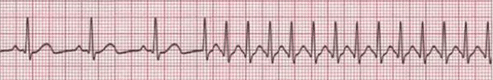
Shockable Rhythms Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular Fibrillation Supraventricular Tachycardia Acls Com

Patient Flow In The Trial Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Was Defined Download Scientific Diagram
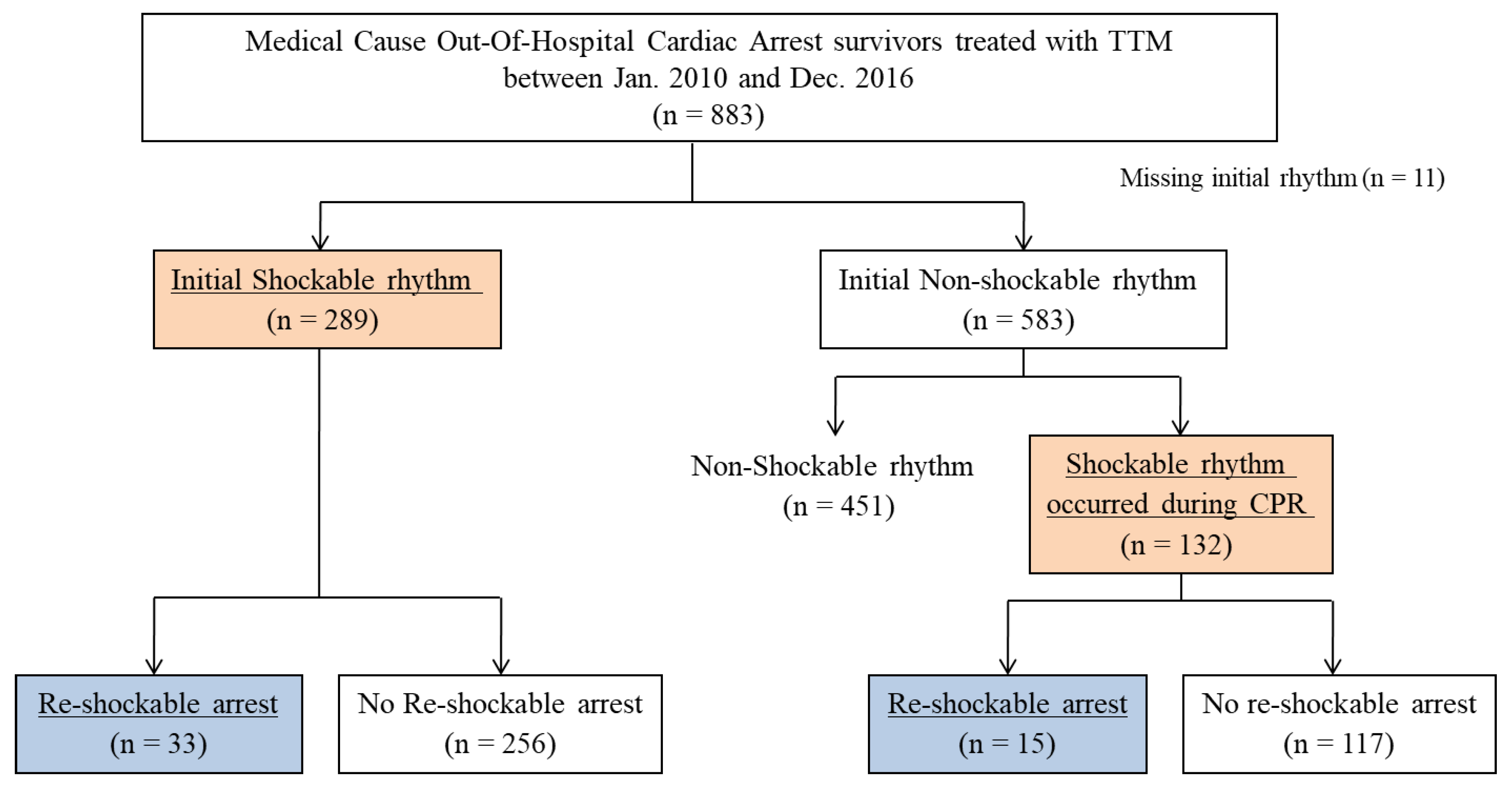
Jcm Free Full Text Prognostic Factors For Re Arrest With Shockable Rhythm During Target Temperature Management In Out Of Hospital Shockable Cardiac Arrest Patients Html

Acls Downloadable Fun Emergency Medicine Board Review
Www Longdom Org Open Access What Is Ventricular Tachycardia For An Automated External Defibrillator 2155 90 5 285 Pdf

Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Acls Com
Mediced Makes It Simple Management Of The Patient In Cardiac Arrest

Acls Cardiac Arrest Vf Pvt And Asystole Pea And Rosc Flashcards Quizlet

Depiction Of Absolute Differences In Survival In The Previously Download Scientific Diagram
Mediced Makes It Simple Management Of The Patient In Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac Arrest Basicmedical Key

Refractory Ventricular Fibrillation Treated With Double Simultaneous Defibrillation Pilot Study

Clinical Predictors Of Shockable Versus Non Shockable Rhythms In Patients With Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Resuscitation

Acls Ventricular Fibrillation And Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Guide

Paediatric Advanced Life Support Pals The Good Doctor

Figure 1 From Association Between Time To Defibrillation And Survival In Pediatric In Hospital Cardiac Arrest With A First Documented Shockable Rhythm Semantic Scholar

Pdf Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Outcomes Stratified By Rhythm Analysis Brian Nathanson Academia Edu
Matters Of The Heart V Tach Patmac Rn

Vf And Pulseless Vt Acls Algorithms Com

Pdf Antiarrhythmic Drugs For Non Shockable Turned Shockable Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest The Amiodarone Lidocaine Or Placebo Study Alps
2
Impact Of Early Intravenous Amiodarone Administration On Neurological Outcome In Refractory Ventricular Fibrillation Retrospective Analysis Of Prospectively Collected Prehospital Data Scandinavian Journal Of Trauma Resuscitation And Emergency
Cpr First Or Defibrillation First Acls Medical Training
Acls Cardiac Arrest Vtach And Vfib Algorithm Acls Medical Training

Prognostic Impact Of The Conversion To A Shockable Rhythm From A Non Shockable Rhythm For Patients Suffering From Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Sciencedirect

Relationships Between Time From Collapse To First Cardiopulmonary Download Scientific Diagram
3

Online American Heart Association Aha Acls Algorithms Acls Recertification Certification Online
Ventricular Fibrillation Vf Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis

Heartify Algorithms Adult Cardiac Arrest Acls Algorithm
Resus Org Au Download Als2 Instructor Clinical Skill Stations Quality Cpr And Defibrillation Quality Cpr And Defibrillation Guidance Jun 16 Pdf

Vf And Pulseless Vt Acls Algorithms Com
Shockable Rhythms Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular Fibrillation Supraventricular Tachycardia Acls Com

Adherence To Guidelines Is Associated With Improved Survival Following In Hospital Cardiac Arrest Sciencedirect

Shockable Rhythms Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular Fibrillation Supraventricular Tachycardia Acls Com

Jmir The Impact Of A Tablet App On Adherence To American Heart Association Guidelines During Simulated Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Randomized Controlled Trial Siebert Journal Of Medical Internet Research

Shockable Rhythms Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular Fibrillation Supraventricular Tachycardia Acls Com
Pediatric Defibrillation After Cardiac Arrest Initial Response And Outcome Critical Care Full Text

Clinical Predictors Of Shockable Versus Non Shockable Rhythms In Patients With Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Sciencedirect
3
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqd5hwdwpwg5ur3ji Zbas6f3i7 0qjfamk Gqtspz Fl9sddo Usqp Cau

Syncope And Cardiac Arrest

Anticipatory Manual Defibrillator Charging During Advanced Life Support A Scoping Review Sciencedirect
Www Resuscitationjournal Com Article S0300 9572 12 4 Pdf

Adherence To Guidelines Is Associated With Improved Survival Following In Hospital Cardiac Arrest Resuscitation
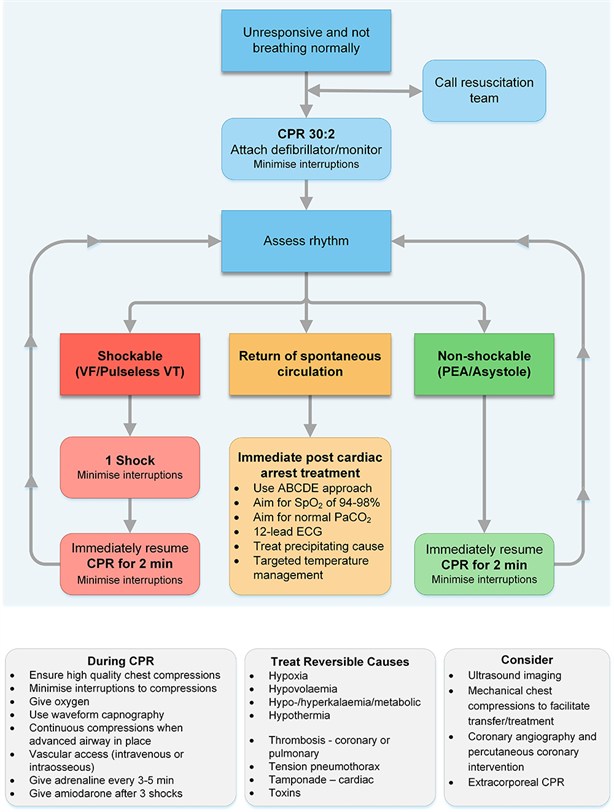
Guidelines Adult Advanced Life Support Resuscitation Council Uk

The Evolving Role Of The Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory In The Management Of Patients With Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest A Scientific Statement From The American Heart Association Circulation
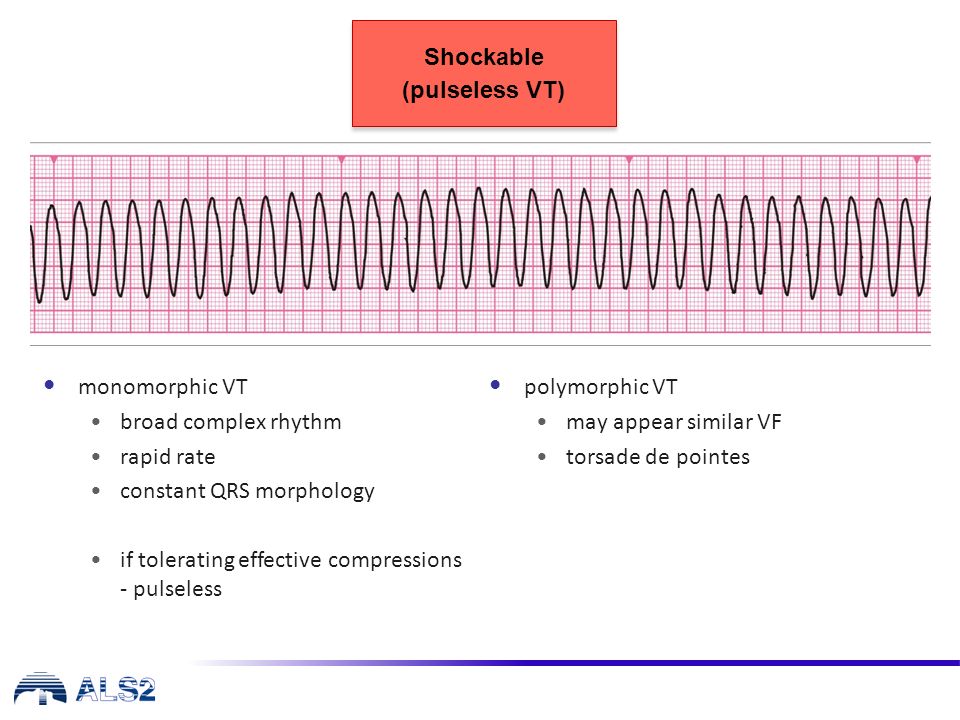
Als Algorithm Ppt Video Online Download

Acls Simplify Algorithm Cardiac Electrophysiology Cardiovascular Physiology
Http Www Jcvaonline Com Article S0735 6757 16 0 Pdf

Utsw Biotel 14 Guidelines For Therapy Asystole
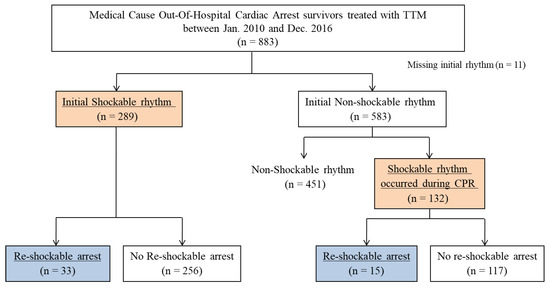
Jcm Free Full Text Prognostic Factors For Re Arrest With Shockable Rhythm During Target Temperature Management In Out Of Hospital Shockable Cardiac Arrest Patients Html
Mediced Makes It Simple Management Of The Patient In Cardiac Arrest

Acls Simplify Algorithm Cardiac Electrophysiology Cardiovascular Physiology

Jmir The Impact Of A Tablet App On Adherence To American Heart Association Guidelines During Simulated Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Randomized Controlled Trial Siebert Journal Of Medical Internet Research

Pdf Subsequent Shockable Rhythm During Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest In Children With Initial Non Shockable Rhythms A Nationwide Population Based Observational Study

Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Acls Algorithms Com

Effect Of Defibrillation Energy Dose During In Hospital Pediatric Cardiac Arrest American Academy Of Pediatrics

Swiss Medical Weekly Outcome After Out Of Hospital Ventricular Fibrillation Or Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Comparison Of Before And After The Implementation Of The 10 Guidelines In A Single Centre
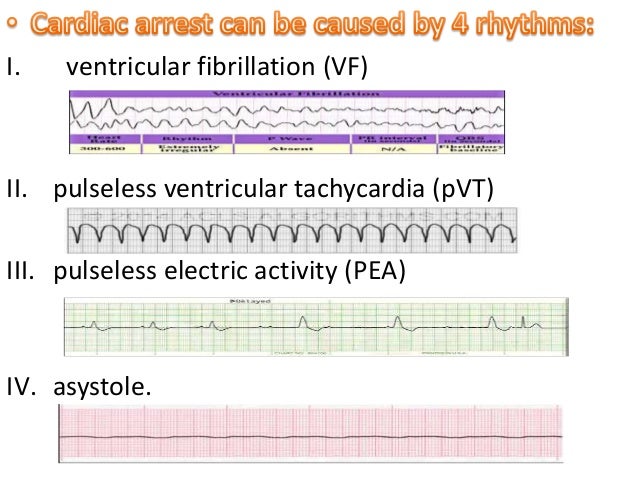
15 Acls
1

Cardiac Arrest Pharmacotherapy A Pathophysiologic Approach 9th Ed

Part 7 Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Circulation

Paediatric Advanced Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Cpr Algorithm Vf Download Scientific Diagram
Http Www Stritch Luc Edu Lumen Meded Elective Er Emorientationacls Coding Pdf

Shockable Cardiac Arrest
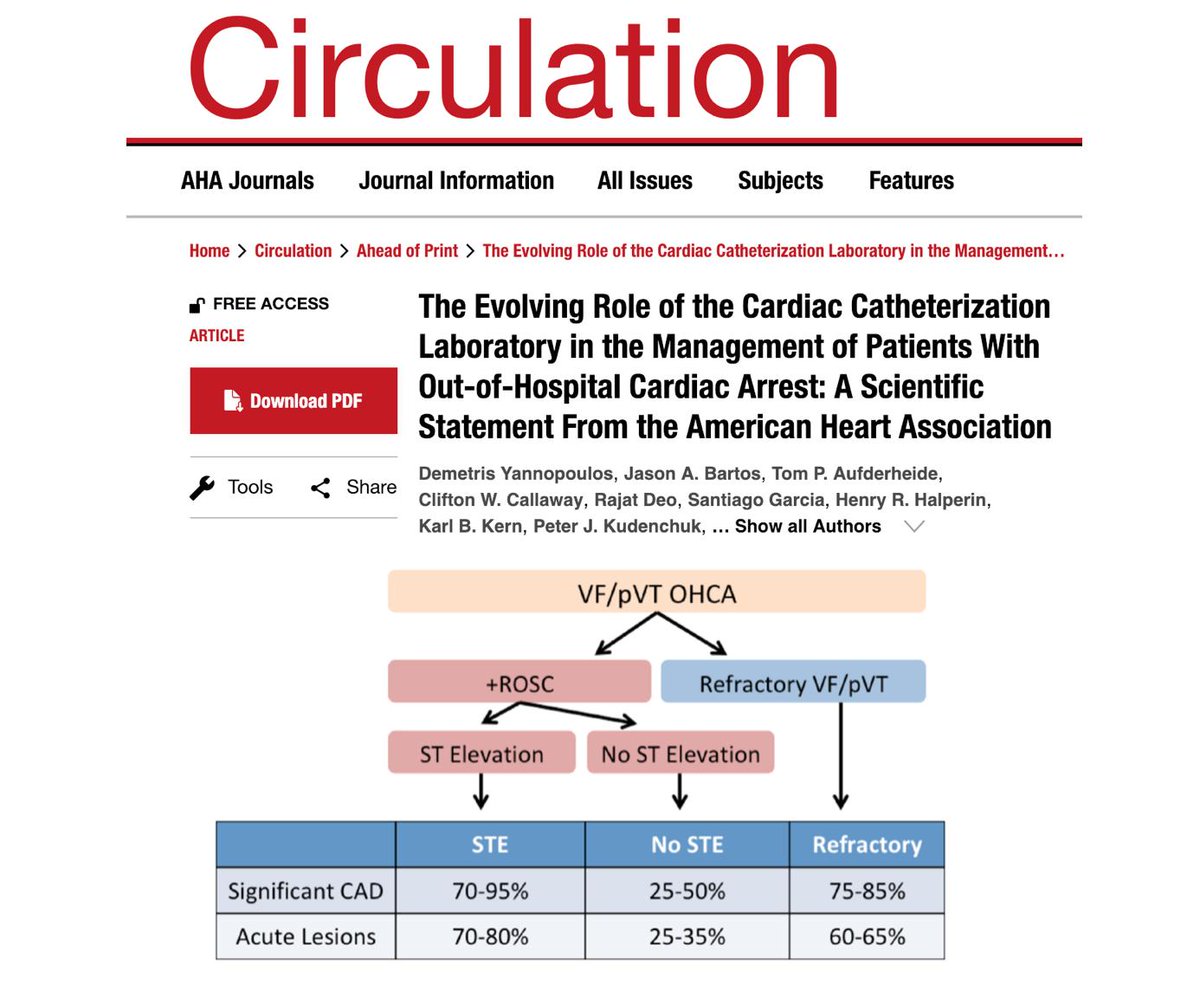
M Velia Antonini Cath Lab Ohca American Heart Statement Cad Prevalent Especially If Shockable Rhythms Vf Pvt Early Access To Coronary Angiography Pci If Refractory Ecmo Support Ecpr Resulted In Functionally Favorable
Non Perfusing Cardiac Rhythms In Asphyxiated Newborn Piglets

Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Acls Algorithms Com

Algorithms American Heart Association Cpr First Aid

Jmir The Impact Of A Tablet App On Adherence To American Heart Association Guidelines During Simulated Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Randomized Controlled Trial Siebert Journal Of Medical Internet Research

Pediatric Defibrillation After Cardiac Arrest Initial Response And Outcome

Acls Cardiac Arrest Vf Pulseless Vt Pvt Pea Asystole Aha 15 Flashcards Quizlet

Conversion To Shockable Rhythms During Resuscitation And Survival For Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Sciencedirect

The Evolving Role Of The Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory In The Management Of Patients With Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest A Scientific Statement From The American Heart Association Circulation

Jkms Journal Of Korean Medical Science



